27/09/2024
Refraction is the eye examination that subjectively measures the patient's refractive error. Refractive error can be defined as the amount of nearsightedness, farsightedness or astigmatism (also called cylinder) in the eye. To determine this, the optician places different lenses in front of the patient's eye with the aim of achieving the highest possible visual acuity, i.e. seeing the smallest possible line of letters. Based on the results of this test, the optician will be able to prescribe glasses or contact lenses.
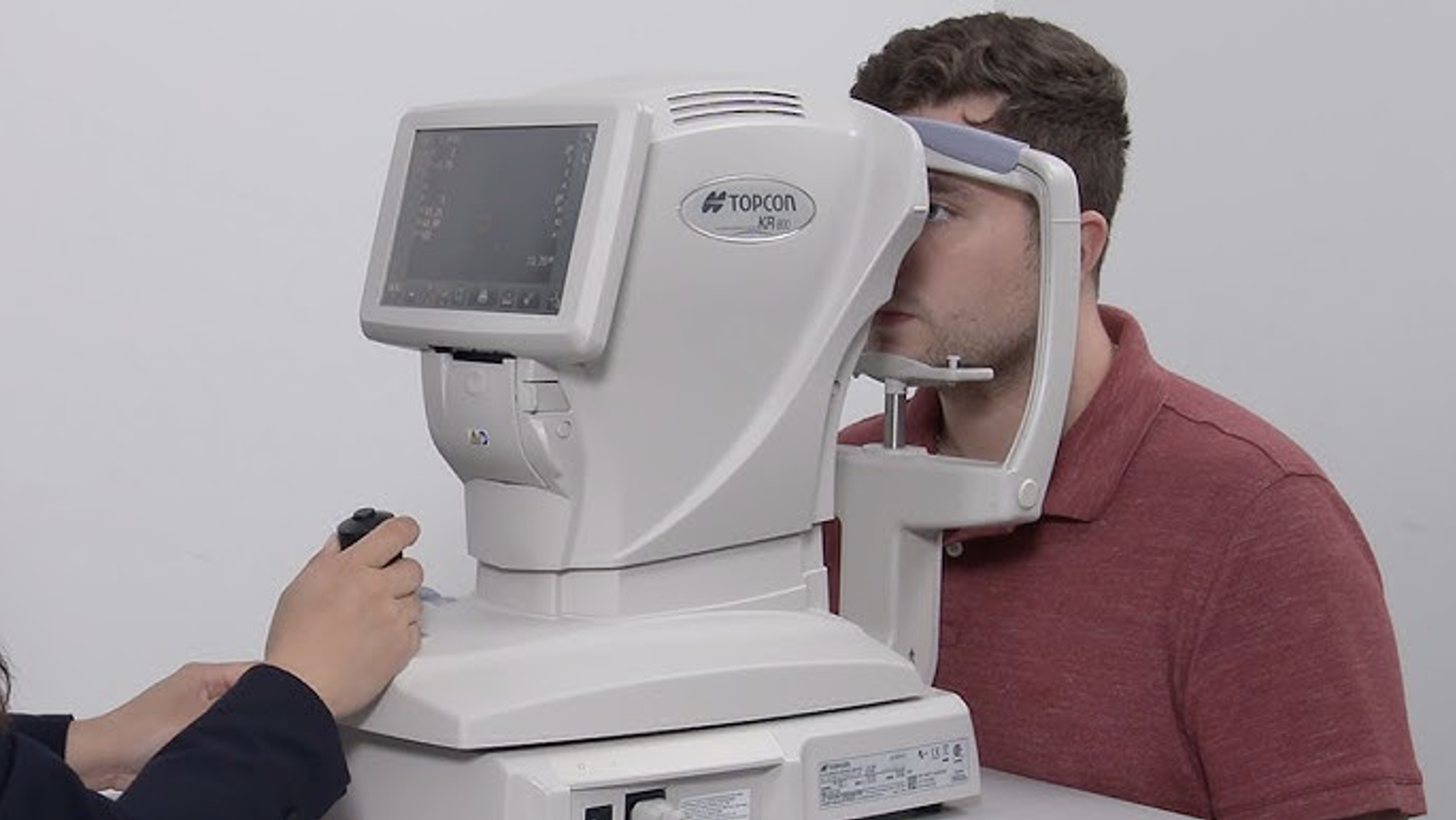
Before starting the subjective examination (based on the patient's answers), an objective refraction is usually carried out using an autorefractometer (see picture below). This gives an approximate refraction value which is used as a starting point for the subjective refraction, saving the optician a lot of time.
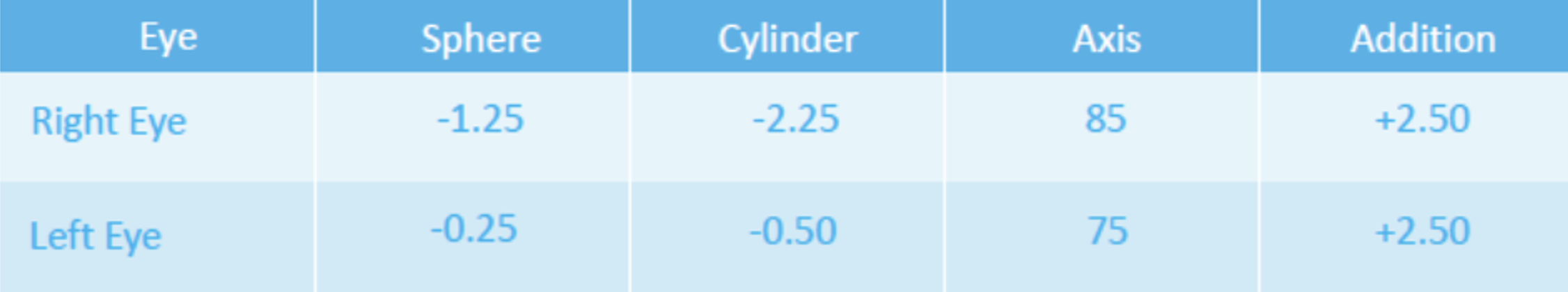
The result of the refraction is mainly expressed by 3 values, usually in the following order Sphere, Astigmatism and Axis. The sphere indicates the amount of myopia or hyperopia the patient has, and the number will be negative to express myopia and positive to express hyperopia. The higher the number (regardless of the sign), the higher the refractive error. For astigmatism, the number will always be negative and, as with the sphere, the higher the number, the higher the astigmatism. Finally, the axis shows the orientation of the astigmatism, which is a very important parameter when making lenses, whether they are spectacles or contact lenses.
The last value that can be expressed in the spectacle prescription is the addition. This value is only present in patients with presbyopia, i.e. the loss of accommodation capacity of the crystalline lens. In simple terms, presbyopia is the condition that doesn't allow us to focus properly on close objects, and it usually appears in our early to mid-40s. This value in the spectacle prescription indicates the additional power needed for this patient to focus on near objects correctly. This value is always positive (usually from +1.00 to +3.00), and the higher the number, the more power is needed.
You are now ready to read and understand a prescription.
So, what is this patient's nearsightedness / farsightedness, astigmatism and addition?