All about the skin around the eyes and “drooping” eyelids
04/04/2025
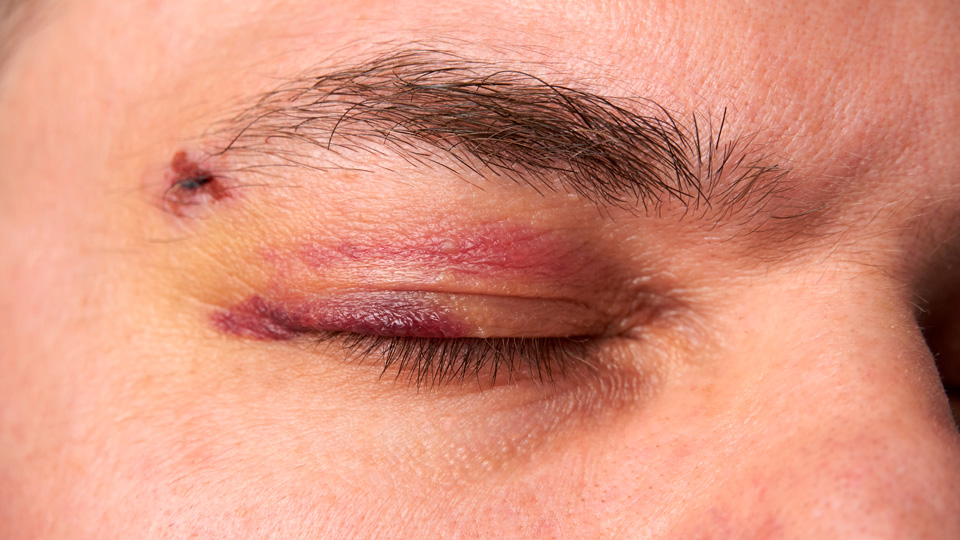
09/07/2024
The orbit is a complex bony structure that houses and protects the eye and its essential components, including muscles, nerves and blood vessels. Orbital fractures can have serious repercussions on ocular health, affecting both visual function and aesthetic appearance. Timely diagnosis and treatment are essential to minimize long-term consequences.
Repercussions on the eye
Orbital fractures can cause various eye problems, depending on the severity and location of the injury.
Diagnosis of orbital fractures generally includes physical examination to evaluate evaluationf ocular mobility, vision, and appearance of the orbit. Diagnostic tests such as computed tomography are also used to evaluate the extent of the fracture and detect any bone displacement or muscle entrapment.
Treatment depends on the severity of the injury and the symptoms presented. An evaluation and surgery, if necessary, should be performed by a specialized oculoplastic surgeon. Conservative treatment with rest, ice application, analgesics and close monitoring is suitable for minor fractures without muscle entrapment or notable ocular subsidence. However, surgery may be required for cases with persistent double vision, significant enophthalmos, muscle entrapment, bone displacement, or to correct aesthetic deformities. Surgery may involve releasing trapped muscles and reconstructing the orbital wall with synthetic materials.
Recovery can range from weeks to months, and ongoing follow-up with an ophthalmologist is essential to monitor recovery and treat any complications. Rehabilitation may include vision therapy to treat diplopia and specific exercises to improve eye mobility.
Thus, orbital fractures can have serious repercussions on ocular health, affecting both visual function and aesthetic appearance. Early diagnosis and proper treatment are crucial to minimize complications and promote a full recovery. Specialized care and close follow-up are essential to ensure the best possible quality of life for affected patients.
Dr. Rob Van der Veen, ophthalmologist at the Barraquer Ophthalmology Centre